Amazon EC2 Installation and Support guide
Instructions for Early Fixpack versions for IBM MQ:
If you are using AWS Images at the following fixpack versions of IBM MQ, please follow these installation instructions:
7.5.*, 8.0.0.*, 9.0.0.*
For all versions 9.1+ continue to follow the instructions on this page.
1. Overview
This guide will provide step by step instructions how to start using the installed products on your AWS EC2 instance.
This AMI contains a ready-to-run MidVision RapidDeploy for MQ Standard and Advanced Editions on AWS base image at the selected version. In order to use this image, you need to launch it with your selected type, and log in via SSH to create and configure required Queue Managers, Queues and Listeners etc.

2. Launching an instance
In order to launch a MidVision RapidDeploy for MQ instance, a few settings need to be configured on the AWS console as follows. The instructions for launching an instance differ depending on where you launch from. Initially you will launch the instance from the AWS Marketplace.
- Select the Product based on your requirements in the AWS Marketplace;
- Click on the link to go to that versions page in AWS Marketplace;
- Check the ‘
Other Versions‘ link to see other versions available (you can select the actual version later). - Under ‘
Pricing Details‘ panel select your Region and either Hourly or Yearly fees. - Click on the ‘
Continue‘, button to go to the ‘1-Click Launch‘ tab on the configuration page; - On the ‘
Software Pricing‘ panel choose your instance type and pricing type; - On the ‘
Version‘ panel, select the fix pack version you require; - On the ‘
Region‘ panel, select the Region you require; - On the ‘
EC2 Instance Type‘ panel, choose the instance type. Them3.mediumtype or larger is recommended when running IBM WebSphere MQ. Larger instances may be required based on the number of IBM WebSphere MQ queue managers etc required and the expected resource use of each; - On the ‘
VPC Settings‘ panel Configure the VPC settings to your requirements or leave the defaults; - On the ‘
Security Group‘ panel, specify the security group. The security group needs to permit to following ports [note that the internal firewall will be configured later to permit only ports used by WebSphere]:Port 22 to connect via SSH (enabled by default), Port 1414 and 1415 to connect to MQ, Port 9090 to reach RapidDeploy web console, Port 9443 to reach IBM MQ web console, Port 20000 and 20100 to open for RapidDeploy Remote Agent (optional)
- If you don’t already have a security group as above, go to your EC2 Control Panel and select ‘
Security Groups‘ under ‘Network & Security‘ - Click ‘
Create Security Group‘ button - To open all ports, Click ‘
Add Rule‘. - In the ‘
Type‘ dropdown, Specify ‘All TCP‘ or your preferred configuration. - In the ‘
Source‘ dropdown, Specify ‘Anywhere‘ or your preferred configuration. Remember to open also ports that will be used by Queue Manager (usually you 1414 and 1415)
- If you don’t already have a security group as above, go to your EC2 Control Panel and select ‘
- On the ‘
Key Pair‘ panel, select a key pair to use. You will need this key later to connect to the instance. - Scroll back to the top of the page and click ‘
Accept Software Terms and Launch with 1-Click‘. - The Instance will be Launched.
- Select the AMI based on your requirements;
- Right click on the AMI, or from the drop down menu, choose the ‘
Launch’ option; - On the ‘
Choose Instance Type‘ tab, choose the instance type.Them3.mediumtype or larger is recommended when running IBM WebSphere MQ. Larger instances may be required based on the number of IBM WebSphere MQ queue managers etc required and the expected resource use of each; Click ‘Next: Configure Instance Details‘. - On the ‘
Configure Instance‘ tab Configure the instance to your requirements or leave the defaults. Click ‘Next: Add Storage‘. - On the ‘
Add Storage‘ tab, add additional storage as required or leave as default. Click ‘Next: Tag Instance‘. - On the ‘
Tag Instance‘ tab, Tag your instance with a suitable name. Click ‘Next: Configure Security Group'. - On the ‘
Configure Security Group‘ tab, specify the security group. The security group needs to permit to following ports:Port 22 to connect via SSH (enabled by default), Port 1414 and 1415 to connect to WMQ, Port 9090 to reach RapidDeploy web console, Port 9443 to reach IBM MQ web console, Port 20000 and 20100 to open for RapidDeploy Remote Agent (optional)
- To open all ports, Click ‘
Add Rule‘. - In the ‘
Type‘ dropdown, Specify ‘All TCP‘ or your preferred configuration. - In the ‘
Source‘ dropdown, Specify ‘Anywhere‘ or your preferred configuration. Remember to open also ports that will be used by Queue Manager (usually you 1414 and 1415)
- To open all ports, Click ‘
- Click ‘
Review and Launch‘. - Review settings, then click ‘
Launch‘. - Add your key pair, Check the ‘Acknowledge key file access’ checkbox and click ‘
Launch Instance‘.
3. Initial login and setup
The products are shipped with a base binary installation but without the necessary Queue Managers created. On the first login to the instance, you will be placed into a console wizard, which will guide you through the process of creating and starting IBM WebSphere MQ Queue Managers and other configuration steps. The following is an overview of the steps you will be guided through to get started with the installed products on the instance.
Once the instance has started up (you can see it by having ” 2/2 checks passed ” in EC2 console).
- Log onto the instance from the EC2 console or via SSH as the ‘
mqm’ user, using the key you selected above. For example:- From the EC2 console by clicking the “
Connect to your instance” button with username “mqm“, using the previously (instance launch-time) selected.pemkeyfile. - Via SSH from your desktop, for example
ssh -i ./MidVisionUSMC.pem mqm@ec2-52-87-198-23.compute-1.amazonaws.com
- From the EC2 console by clicking the “
- You should see the MidVision banner and then you are placed in a setup wizard.
Welcome to __ __ _ ___ ___ _ ____ _ _ | \/ (_) __| \ \ / (_)___(_) ___ _ __ / ___| | ___ _ _ __| | | |\/| | |/ _` |\ \ / /| / __| |/ _ \| '_ \ _____| | | |/ _ \| | | |/ _` | | | | | | (_| | \ V / | \__ \ | (_) | | | |_____| |___| | (_) | |_| | (_| | |_| |_|_|\__,_| \_/ |_|___/_|\___/|_| |_| \____|_|\___/ \__,_|\__,_| A MidVision Service * WebSite: https://www.midvisioncloud.com/ibm-websphere-on-amazon-web-services/ * Support: http://support.midvision.com/redmine/projects/devtestcloud * Forum: https://www.midvisioncloud.com/community Welcome, this is MidVisionCloud RapidDeploy and IBM WebSphere MQ image first run configuration. Configuration steps - Create and Start a default IBM MQ web console - Set RapidDeploy framework initial password - Open ports on RHEL firewall Create and Start default IBM MQ Web Console? [y/n] - On the first login to the instance, you will be placed into a console wizard, which will guide you through the process of creating and configuring IBM WebSphere MQ. After logging onto the instance via SSH as the ‘mqm’ user you will be placed in a setup wizard. The following is an overview of the steps you will be guided through to create the required profiles on the instance:
- Create and Start a default IBM MQ web console.
- Set initial password for RapidDeploy user “mvadmin”.
- Choose which ports to open on Red Hat Linux firewall. You should open port 9090 for the RapidDeploy web console if required. You should open the required ports for MQ, typically 1414 and 1415.
All inputs asking for specific data can be left as blank just by hitting
[return], which will pick the default value displayed at the end of the question. Please refer to IBM documentation for WebSphere MQ configuration. - If you choose default options you should see this information:
Configuration finished, you may now start using RapidDeploy services and other software. Web user interfaces are available on: IBM MQ Web Console: https://ec2-52-206-103-87.compute-1.amazonaws.com:9443/ibmmq/console (web console credentials: mqadmin/i-0e5b506ae1cfa1790) RapidDeploy: ec2-52-206-103-87.compute-1.amazonaws.com:9090/MidVision
4. Accessing the web and command line consoles
4.1 Access the IBM MQ Web Console
If you choose to create and start IBM MQ Web Console then you can access it on:https://[publicip]:9443/ibmmq/consoleNote: make sure you have port 9443 open in your Security group when trying to access IBM MQ web console. Your password for the default username ‘
mqadmin ‘ is set to instance-id but you can change it by just editing a file
/var/mqm/web/installations/Installation1/servers/mqweb/mqwebuser.xmland restarting web console:
[mqm] endmqweb [mqm] strmqweb
4.2 Subsequent logins via SSH to the instance
When logging into the instance after the first time, you will be asked if you wish to enter the console menu. Selecting ‘y‘ places you in a management console. Selecting ‘n‘ will take you to a command prompt. You can access the menu at any time by typing ‘menu’ at the command prompt. In the menu context, after first login you can perform the following actions:
- Create a default configuration
- Display IBM MQ installation details
- Manage IBM MQ – this option is very helpful and lets you create/manage/delete queue managers, listeners, channels and queues
- Open Firewall Port if you wish. Usually you will need to open ports 1414 and 1415
Main Application Administration Menu on ip-172-31-44-143 ======================================================== Please select from list 1. Create a default configuration 2. Display Status for ip-172-31-44-143 3. Manage IBM MQ 4. Open Firewall Port on ip-172-31-44-143 5. Help for the Management menu x. Quit >1
If you would like to create a default basic MQ configuration to be able to quickly connect to your MQ instance, then select the first option. You will be asked to provide the name for the default QM, name of the listener, port for listener and finally the name of the default Channel
Define a new Queue Manager Please type the name of Queue Manager or submit blank for default value 'QMGR1' QMGR1 Define a new listener Please provide the name of the new Listener or submit blank for default value 'QMLIST1' QMLIST1 Please provide the port of the new Listener or submit blank for default value '1414' 1414 Define a new Channel Please provide the name of the new Channel or submit blank for default value 'QMCHNL1' DEFAULTCHANNEL
Then you should be able to see the confirmation that the default configuration has been created:
The default configuration has been created and it is running now. See connection details below: Public hostname: ec2-34-204-70-157.compute-1.amazonaws.com Queue Manager: QMGR1 Port: 1414 Server connection channel: DEFAULTCHANNEL
Use these QM details to obtain connection between your MQ Client and this newly created and started Queue Manager. For example in WebSphere Application Server :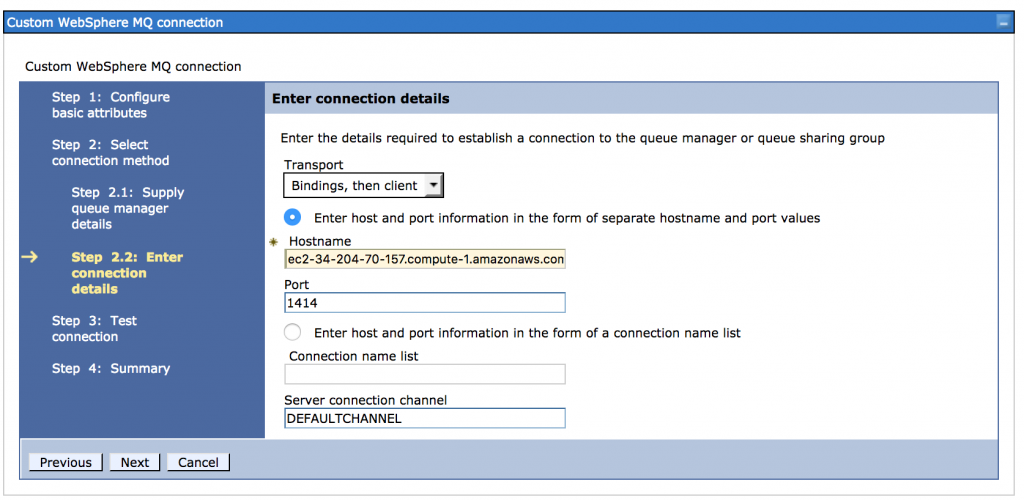
If you have any problems with connecting to the default QM please take a look at the Troubleshooting section.
4.3 Sample configuration created using our menu script
We prepared sample configuration of WMQ for you. Following the steps below you will create two queue managers with local and remote queues, then you will define listeners and channels that will allow communication between these queue managers.
1. Select Manage IBM MQ from main menu and Create new Queue Managers with names QMGRA and QMGRB 2. Select QMGRA and then select option 5 to start it. 3. You can check if QMGRA is running using option 6 4. Select Manage Queues option for QMGRA and select option 2 to define new transmission queue (name: QMGRB.XMIT.DF, init queue name: SYSTEM.CHANNEL.INITQ) 5. Now select option 1 to define new local queue (name:QMGRB.QMGRA.RQSTIN) 6. Using option 5 to define new remote queue (name: QMGRA.QMGRB.RQST, transmission queue: QMGRB.XMIT.DF, remote queue: QMGRA.QMGRB.RQSTIN, queue manager: QMGRB) 7. Leave current menu using x. Quit option and select Manage Channels for QMGRA 8. Define Sender Channel (name: QMGRA.QMGRB.DF, transmission queue name: QMGRB.XMIT.DF, ip address: localhost, port: 1414) 9. Define Receiver Channel (name: QMGRB.QMGRA.DF) 10. Leave current menu and select Manage Listener 11. Define new Listener (name: LISTENER.TCP.QMGRB, port: 1415) 12. Go to main menu and Select Queue Manager QMGRB 13. Start QMGRB and then go to Manage Queues for this queue manager 14. Define Transmission queue (name: QMGRA.XMIT.DF, init queue name: SYSTEM.CHANNEL.INITQ) 15. Define Local queue (name: QMGRA.QMGRB.RQSTIN) 16. Define Remote queue (name: QMGRB.QMGRA.RQST, transmission queue name: QMGRA.XMIT.DF, remote queue: QMGRB.QMGRA.RQSTIN, queue manager: QMGRA) 17. Go to Manage Channels option for QMGRB and define new Sender Channel (name: QMGRB.QMGRA.DF, transmission queue name: QMGRA.XMIT.DF, ip address: localhost, port 1415) 18. Define Receiver Channel for QMGRB: (name: QMGRA.QMGRB.DF) 19. Go to Manage Listeners for QMGRB and define new Listener (name: LISTENER.TCP.QMGRA, port: 1414) 20. Use option 3 to Start Listener (select LISTENER.TCP.QMGRA) and then use option 5 to Display status of Listeners for QMGRB 21. Go to main menu and now select QMGRA 22. Go to Manage Listeners and start Listener LISTENER.TCP.QMGRB 23. Go to Manage Channels for QMGRA and Start Channel: QMGRA.QMGRB.DF 24. Select Queue Manager QMGRB, go to Manage Channels and Start Channel: QMGRB.QMGRA.DF)
Of course you can still use all the commands directly from WMQ without using our prepared menu.
4.4 Access the RapidDeploy Web Console
RapidDeploy server and agent will start up automatically when you start your instance. You can access the web console on:
http://[publicip]:9090/MidVision
Note: make sure you have port 9090 open in your Security group when trying to access RapidDeploy web console. For the first time, you can set the password for the default username ‘ mvadmin ‘.
5. Maintaining the installation
- mqm: This is the default user, which you can log in as. It is permitted to use all SUDO rights. To switch to the root user, type “
sudo su“. - root: This is the superuser in linux systems. You can log in as any other user without using passwords. E.g: “
su ec2-user“, “su mqm“ - ec2-user: This user does not have SUDO rights. If you want to switch back to root user, type “
exit“, this will take you back to the previous user session.
RHEL instances are shipped with a firewall by default to protect your machine. For security reasons, the instance is only accessible via SSH (port 22) at first, so further ports can be opened on the firewall as needed. You will need to open all the ports in this internal firewall, which you have open in your Security group. There is a script placed in the user home of the mqm user (/home/mqm), which is also the starting location when logged in. You will need to be the root user to run this script. Example usage:
[mqm@ ] sudo ./open-firewall.sh 9090 Open firewall port 9090 iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ]
There are a few scripts and other files in mqm and root users home directory, which will need to remain unchanged in order to keep the provided scripts working. There are a set of scripts in mqm home directory. Those scripts are executed when logging into the instance controlled by .bash_profile , but you can also execute them manually whenever they are needed. There are some hidden files used as well, .firstrun indicates that the setup wizard has already ran once.
To restart RapidDeploy manually from the filesystem, use the rapiddeploy linux service. The RapidDeploy version is 5.0.5. RapidDeploy home is located at /var/rd/midvision Example usage:
[mqm@ ] sudo service rapiddeploystart start [mqm@ ] sudo service rapiddeploystart stop
The RapidDeploy server uses an in-memory database, so your RapidDeploy framework needs to be shut down properly to save your work. This happens when the instance is stopping or when calling the stop service manually from the command line. Note that on instance restart, unsaved data will be lost.
Before upgrading your MQ installation we strongly recommend creating a backup so you can be sure you have working installation if anything goes wrong during the upgrade process.
Also note that this instruction is only for single MQ installation and only for minor upgrades (for example the scenario here is to upgrade to the latest 9.1 version). If you have more advanced scenarios or you would like to migrate to the latest major release – we recommend contacting us and use our consultancy services.
Login to the instance as mqm user and follow this example:
- Stop all the queue managers and stop IBM MQ web console (endmqweb command)
- Follow these commands:
sudo su cd /home/mqm mkdir binaries cd /home/mqm/binaries/ [obtain download link from midvision support to use in next step] curl "https://ibm-binaries-for-ami.s3.amazonaws.com/ibm/mq/v91/lin/9.1.0-IBM-MQ-LinuxX64-FP0016.tar.gz?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20230818T050755Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Expires=604799&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAI2TAAKASMQJGdsdasdQSQ%2F20230818%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Signature=751a4a461dc2ede80ec1408e5547d196eb49a25a26d0ddf5f7d27438566b6d17" -o 9.1.0-IBM-MQ-LinuxX64-FP0016.tar.gz tar -xvf 9.1.0-IBM-MQ-LinuxX64-FP0016.tar.gz [remove not installed packages which are for Advanced edition only - if your installation is Advanced skip the next step] rm -rf MQSeriesXRService-U* MQSeriesFTAgent-U* MQSeriesFTBase-U* MQSeriesFTLogger-U* MQSeriesFTTools-U* MQSeriesFTService-U* MQSeriesAMS-U* MQSeriesAMQP-U* rpm -ivh *.rpm
This way your MQ installation should be upgraded. You can now start the queue managers.
For security reasons, you will need to change the default password (default value is ‘[instance-id]‘) for user mvadmin. This will be requested the first time only when you log in to the RapidDeploy server.
6. Troubleshooting
6.1 Session loss during setup
If you lose your SSH connection to the target instance during the first run setup script execution (e.g. as a result of a network problem), we advise you to delete and recreate the EC2 instance and run the script again.
6.2 Problem with the connection to Queue Manager
Common ERRORS and issues with obtaining connection:
- MQRC_UNKNOWN_CHANNEL_NAME
– you need to make sure the QM is actually running and the channel you selected exists. Some of the MQ clients like WAS for example require capital letters in configuration, so for example even if your channel name is “defaultChannel” you need to put “DEFAULTCHANNEL” in your MQ Client
– check if your Listener port is correct and if the Listener has Running status
- MQRC_NOT_AUTHORIZED
Usually it happens because of the following reasons:
– CHLAUTH parameter is enabled in your QM configuration. Disable this parameter if you don’t need it or read more about this attribute on IBM documentation pagesrunmqsc QMGR1 display QMGR ALTER QMGR CHLAUTH(DISABLED) end
– the MQ Client user is not permitted to connect to QM
[mqm@ip-172-30-0-167 ~]$ setmqaut -m QMGR1 -t qmgr -g root +all
– the MQ Client requires the user to have password. In our instance there is no password set for mqm user but you can easily change it
[mqm@ip-172-31-2-146 ~]$ sudo su [root@ip-172-31-2-146 mqm]# passwd mqm New password: Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
6.3 gsk8capicmd_64 command not available
[mqm@ip-172-31-1-61 ~]$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH+=":/opt/mqm/gskit8/lib:/opt/mqm/gskit8/lib64" [mqm@ip-172-31-1-61 ~]$ /opt/mqm/gskit8/bin/gsk8capicmd_64Also, you can add the gskit8 bin directory to the PATH variable, then instead of the full path of the binary, you can just run the command gsk8capicmd_64:
[mqm@ip-172-31-1-61 ~]$ export PATH+=":/opt/mqm/gskit8/bin" [mqm@ip-172-31-1-61 ~]$ gsk8capicmd_64
6.4 kernel: drbd: module verification failed: signature and/or required key missing – tainting kernel
When you use MQ Advanced edition you will see these errors in /var/log/messages :
Mar 8 12:59:55 ip-172-30-2-152 kernel: drbd: loading out-of-tree module taints kernel. Mar 8 12:59:55 ip-172-30-2-152 kernel: drbd: module verification failed: signature and/or required key missing - tainting kernel
We contacted Red Hat and we confirmed this is doesn’t affect MQ Advanced functionality.
The kernel signs all of the modules that are supplied by Red Hat in order to determine
whether the system has an out-of-the-box module [i.e., third party] loaded. It is merely
an informational message and doesn’t cause any harm by itself.
Simply put, messages of this kind are expected while using driver modules [third party]
that are provided by vendors other than Red Hat (IBM in this case). These messages are helpful while
debugging issues in later stages.
6.5 Contacting MidVision support
Please visit our support website.
